In its most recent report on the global economic outlook, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) forecasts that global economic growth will remain resilient, although economic recovery is likely to take longer than previously expected.
Despite a challenging global environment due to conflicts in the Middle East and a slowdown in global growth, the Dominican economy maintains favorable forecasts for the years 2024 and 2025, according to a report by Página Abierta authored by Osvaldo Lagares from the Department of Regulation and Financial Stability of the Central Bank (BCRD).
The publication titled “Growth and Stability Perspectives in the Dominican Republic” emphasizes that the Dominican economy exhibits a better investment climate and greater economic and financial stability compared to previous years and during the Covid-19 pandemic.
“Productive activities have expanded, inflationary pressures have eased, and employment has increased to historic levels, promoting stability, growth, and national economic development,” he states.
According to the author, this economic performance has contributed to improvements in the country’s credit rating outlook published by major international rating agencies.
“In this regard, the Emerging Markets Bond Index (EMBI) for the Dominican Republic, calculated by the U.S. financial services firm JPMorgan Chase, which serves as a benchmark for country risk in emerging and developing economies, is 32.5% below the regional average for Latin America and 22.6% below the global average, at levels lower than economies such as Mexico, Colombia, and Panama,” he adds.
The main economic outlook for the Dominican Republic in 2024 suggests that economic growth will return to its potential path of 5.0%, inflation will remain around the center of the policy target range of 4.0% ± 1.0%, and interest rates will trend downwards if risk factors do not intensify.
Additionally, it is expected that the exchange rate will remain relatively stable around its historical average variation, given the foreign exchange earnings received by the country, with projections indicating these earnings will exceed those of 2023, when remittance flows reached US$10.1572 billion, tourism revenues amounted to US$9.8289 billion, and foreign direct investment totaled US$4.381 billion.
Furthermore, the adoption of macroprudential policies and proper management of financial intermediaries’ liquidity to reduce systemic risk and facilitate the channeling of resources to productive sectors, households, and SMEs, will contribute to expanding credit and revitalizing the economy in an environment of price stability and financial system stability.
Recent Domestic Environment
The timely adoption of monetary and financial policies in the country has contributed to inflation converging faster than expected to 3.57% in 2023, with core inflation at 4.32%, aiming towards the center of the policy target range and expected to remain around this level through 2024.
Following the achievement of inflation convergence to the target range, the central bank began gradually reducing the reference rate starting in May 2023, totaling a decrease of 150 basis points to reach 7.00% by December 2023.
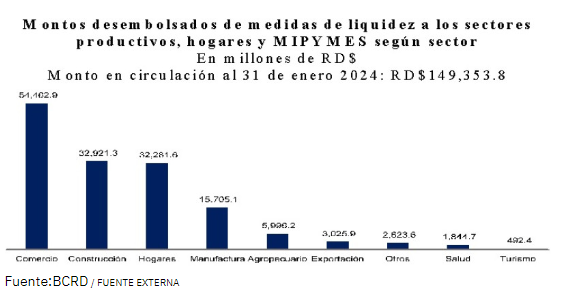
In addition to these monetary measures, a liquidity provision program has been implemented through the release of legal reserve requirements and the Quick Liquidity Facility (FLR), through which financial intermediaries have channeled loans totaling approximately RD$190 billion to productive sectors, households, micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs), at interest rates of up to 9% per year. Currently, around RD$30 billion remains in circulation for liquidity management by financial intermediaries, while RD$149,353.8 billion has been directed to productive sectors, households, and MSMEs, benefiting economic agents with over 27,600 loans and contributing to stimulating productive activities in a stable financial environment.
Furthermore
The gross domestic product (GDP) per capita of the Dominican Republic reached US$11,200 by the end of 2023, placing it as a middle-income economy and the seventh largest in Latin America.
Exchange market stability has been maintained, with the spot market selling rate for the US dollar showing a year-on-year depreciation of just 3.3% by the end of 2023, below the pre-pandemic five-year average of 3.6%.
As of December 2023, total assets of financial intermediaries reached RD$3.50 trillion (51.4% of GDP), and the loan portfolio amounted to RD$1.93 trillion, showing a growth of 19.6%.
The credit portfolio’s risk profile remains historically low, with a delinquency rate around 1.2% and a provision coverage ratio of 267%, indicating that financial intermediaries have ample resources to cover more than the entirety of overdue loans.
The net worth of financial intermediaries has strengthened by over RD$54.935 billion, reaching 5.9% of GDP, reflecting increases in paid-up capital and strong performance in financial results. Return on assets (ROA) increased from 2.6% in 2022 to 3.1% by December 2023, while return on equity (ROE) rose from 23.0% to 26.4%, respectively.
Public confidence in financial institutions remains strong, with public deposits increasing by 22.2% to RD$2.6 trillion by the end of 2023, while multiple banks maintained public deposits in foreign currency totaling approximately US$12.1 billion, marking an unprecedented milestone in recent years.
Overall, systemic risk levels have decreased, and the availability of foreign currency liquidity has been maintained to promote stability and growth.
Source:



